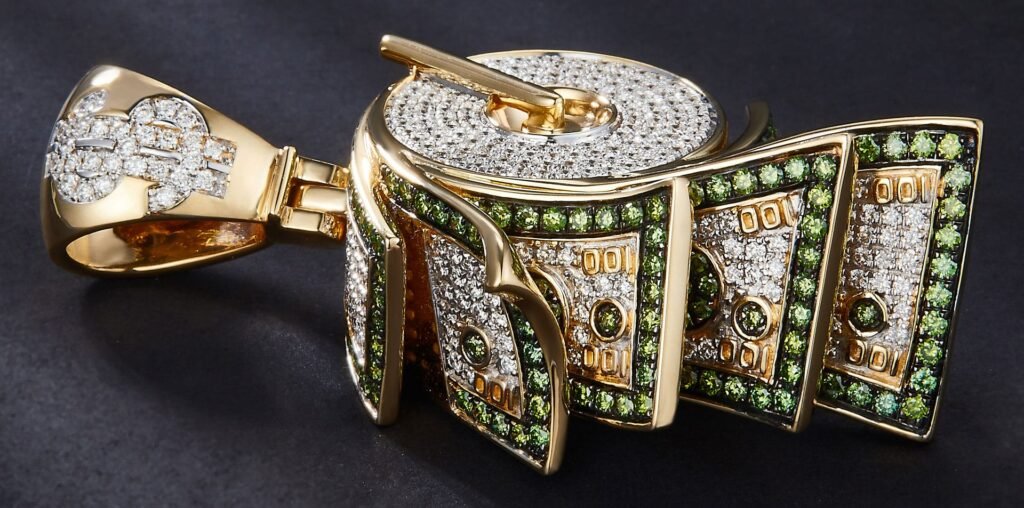
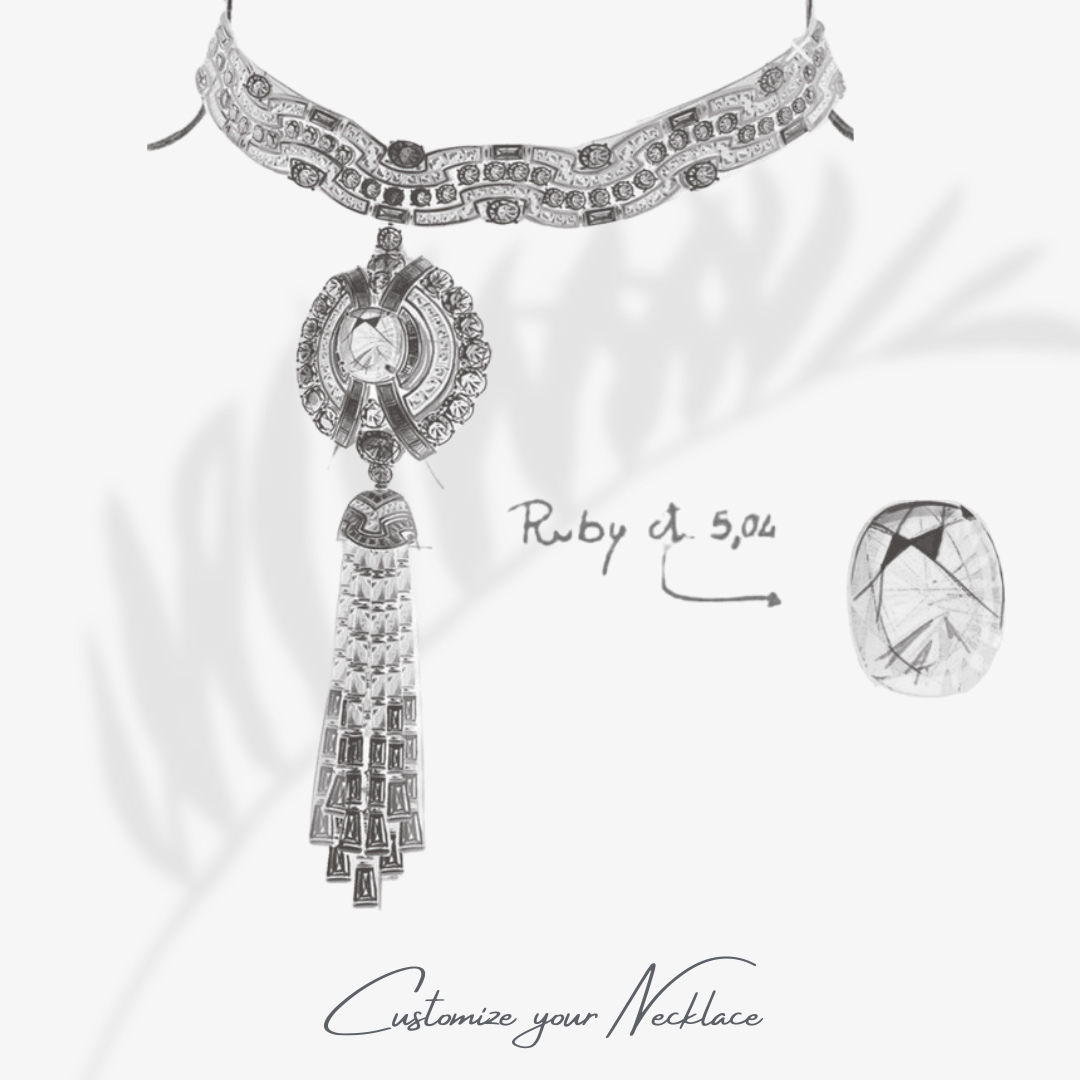
Air pollution, dirt, and daily wear can dull the surface of your jewelry and cloud the brilliance of gemstones. Regular cleaning and proper care are essential to maintain the shine and beauty of your pieces. This guide provides detailed instructions on how to clean various types of jewelry at home, ensuring they remain in pristine condition. By following these guidelines, you can keep your jewelry looking beautiful and well-maintained for years to come.









- Store Properly: Keep jewelry in a cool, dry place, preferably in a jewelry box with separate compartments to avoid scratches.
- Insure Valuables: Consider insuring valuable jewelry to protect against loss, theft, or damage. Keep an inventory with photos and appraisals.
- Remove During Activities: Take off jewelry during activities that could expose it to chemicals, abrasives, or impact, such as swimming, cleaning, or exercising.
- Avoid Ultrasonic Cleaning at Home: Ultrasonic cleaners can damage delicate jewelry and loosen stones. It’s best to leave ultrasonic cleaning to professionals.
- Select Metals Wisely: Different metals require varying levels of care. Consider your lifestyle and maintenance preferences when choosing jewelry. Durable metals such as platinum are great for those with active lifestyles.
- Check Settings Regularly: Inspect your jewelry regularly for loose stones or damaged settings and get them repaired promptly.
- Keep Away from Chemicals: Avoid exposing jewelry to household chemicals, perfumes, and lotions, as they can cause damage and discoloration.
- Polish Softly: Use a soft, lint-free cloth to polish jewelry and maintain its shine.
- Clean Regularly: Make a habit of cleaning your jewelry regularly to prevent dirt buildup and tarnish.
- Handle with Care: Always handle jewelry gently, especially pieces with delicate gemstones or intricate designs.
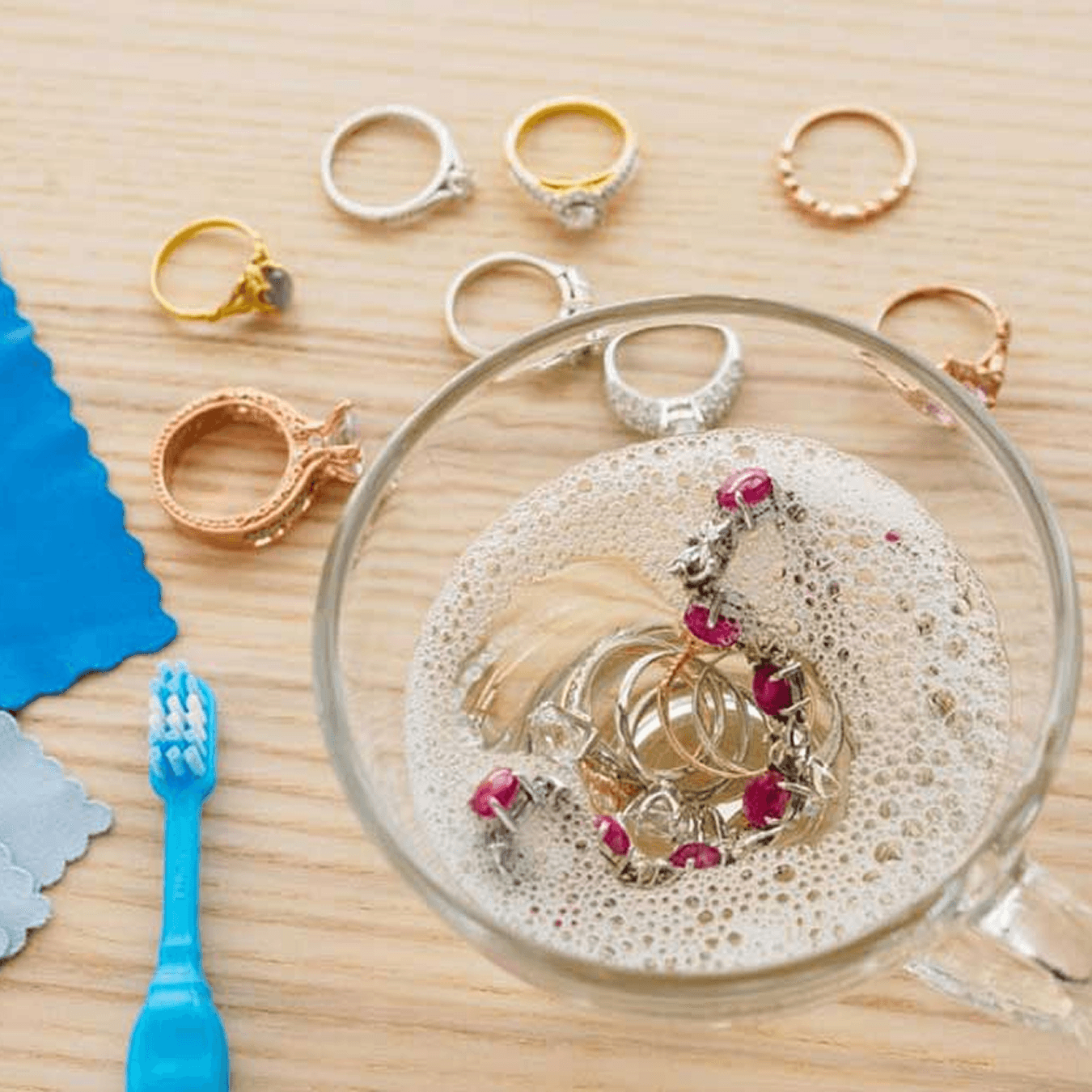


- Store Properly: Keep jewelry in a cool, dry place, preferably in a jewelry box with separate compartments to avoid scratches.
- Insure Valuables: Consider insuring valuable jewelry to protect against loss, theft, or damage. Keep an inventory with photos and appraisals.
- Remove During Activities: Take off jewelry during activities that could expose it to chemicals, abrasives, or impact, such as swimming, cleaning, or exercising.
- Avoid Ultrasonic Cleaning at Home: Ultrasonic cleaners can damage delicate jewelry and loosen stones. It’s best to leave ultrasonic cleaning to professionals.
- Select Metals Wisely: Different metals require varying levels of care. Consider your lifestyle and maintenance preferences when choosing jewelry. Durable metals such as platinum are great for those with active lifestyles.
- Check Settings Regularly: Inspect your jewelry regularly for loose stones or damaged settings and get them repaired promptly.
- Keep Away from Chemicals: Avoid exposing jewelry to household chemicals, perfumes, and lotions, as they can cause damage and discoloration.
- Polish Softly: Use a soft, lint-free cloth to polish jewelry and maintain its shine.
- Clean Regularly: Make a habit of cleaning your jewelry regularly to prevent dirt buildup and tarnish.
- Handle with Care: Always handle jewelry gently, especially pieces with delicate gemstones or intricate designs.
Advantages: Lab-grown diamonds are typically more affordable than natural diamonds, are guaranteed conflict-free, and have a lower environmental impact. They offer the same beauty and brilliance as natural diamonds.
Disadvantages: Some perceive natural diamonds to have a higher resale value and emotional significance due to their rarity and natural formation over millions of years.
The future of lab-grown diamonds looks promising, with increasing demand driven by ethical considerations and sustainability. As technology advances, production costs may continue to decrease, making lab-grown diamonds more accessible. They are expected to gain more market share as consumers prioritize ethical and environmentally friendly options.
Companies use two main methods to create lab-grown diamonds: High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Both methods simulate the natural conditions under which diamonds form, creating real diamonds that are chemically and physically identical to those mined from the earth.
The primary difference is their origin. Lab-grown diamonds are created in controlled laboratory environments, while natural diamonds are formed over millions of years deep within the earth. Both are chemically, physically, and optically identical, with lab-grown diamonds often being more affordable and ethically sourced.